What Does it Take to Be a Mining or Geological Engineer?
Example of Mining or Geological Engineer Job Conduct sub-surface surveys to identify the characteristics of potential land or mining development sites. May specify the ground support systems, processes and equipment for safe, economical, and environmentally sound extraction or underground construction activities. May inspect areas for unsafe geological conditions, equipment, and working conditions. May design, implement, and coordinate mine safety programs.
List of Mining or Geological Engineer Job Duties
- Implement and coordinate mine safety programs, including the design and maintenance of protective and rescue equipment and safety devices.
- Select locations and plan underground or surface mining operations, specifying processes, labor usage, and equipment that will result in safe, economical, and environmentally sound extraction of minerals and ores.
- Devise solutions to problems of land reclamation and water and air pollution, such as methods of storing excavated soil and returning exhausted mine sites to natural states.
- Design, develop, and implement computer applications for use in mining operations such as mine design, modeling, or mapping or for monitoring mine conditions.
- Select or devise materials-handling methods and equipment to transport ore, waste materials, and mineral products efficiently and economically.
- Inspect mining areas for unsafe structures, equipment, and working conditions.
Featured schools near , edit
Skills Needed to be a Mining or Geological Engineer
Mining and Geological Engineers state the following job skills are important in their day-to-day work.
Complex Problem Solving: Identifying complex problems and reviewing related information to develop and evaluate options and implement solutions.
Critical Thinking: Using logic and reasoning to identify the strengths and weaknesses of alternative solutions, conclusions or approaches to problems.
Writing: Communicating effectively in writing as appropriate for the needs of the audience.
Speaking: Talking to others to convey information effectively.
Judgment and Decision Making: Considering the relative costs and benefits of potential actions to choose the most appropriate one.
Reading Comprehension: Understanding written sentences and paragraphs in work related documents.
Types of Mining or Geological Engineer
- Mine Safety Engineer
- Project Engineer
- Planning Engineer
- Mine Exploration Engineer
- Mine Engineering Manager
Is There Job Demand for Mining and Geological Engineers?
In the United States, there were 7,300 jobs for Mining or Geological Engineer in 2016. New jobs are being produced at a rate of 8.2% which is above the national average. The Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts 600 new jobs for Mining or Geological Engineer by 2026. The BLS estimates 600 yearly job openings in this field.

The states with the most job growth for Mining or Geological Engineer are North Dakota, Colorado, and Tennessee. Watch out if you plan on working in Kentucky, Utah, or Wyoming. These states have the worst job growth for this type of profession.
Do Mining and Geological Engineers Make A Lot Of Money?
The typical yearly salary for Mining and Geological Engineers is somewhere between $54,550 and $151,030.
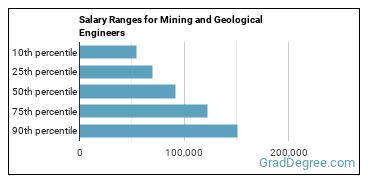
Mining and Geological Engineers who work in California, New Mexico, or Florida, make the highest salaries.
How much do Mining and Geological Engineers make in each U.S. state?
| State | Annual Mean Salary |
|---|---|
| Alabama | $97,670 |
| Alaska | $112,110 |
| Arizona | $81,150 |
| California | $123,060 |
| Colorado | $108,130 |
| Florida | $113,200 |
| Idaho | $74,990 |
| Illinois | $92,530 |
| Indiana | $72,840 |
| Kentucky | $94,810 |
| Maryland | $76,360 |
| Michigan | $78,700 |
| Minnesota | $101,710 |
| Nevada | $85,640 |
| New Mexico | $140,130 |
| New York | $90,240 |
| North Dakota | $80,350 |
| Ohio | $89,260 |
| Oregon | $76,810 |
| Pennsylvania | $90,510 |
| Utah | $93,580 |
| Washington | $99,490 |
| West Virginia | $76,050 |
| Wyoming | $93,990 |
What Tools do Mining and Geological Engineers Use?
Below is a list of the types of tools and technologies that Mining and Geological Engineers may use on a daily basis:
- Microsoft Excel
- Microsoft Word
- Microsoft Office
- Microsoft PowerPoint
- Microsoft Access
- Microsoft Project
- Autodesk AutoCAD
- Statistical software
- Oracle Primavera Systems
- Carlson SurvCADD
- Maptek Vulcan
- MineSight
- Trimble Geomatics Office
- Gemcom Surpac
Becoming a Mining or Geological Engineer
What kind of Mining or Geological Engineer requirements are there?

How many years of work experience do I need?

Where Mining and Geological Engineers Are Employed

The table below shows the approximate number of Mining and Geological Engineers employed by various industries.

Related Careers
Those interested in being a Mining or Geological Engineer may also be interested in:
References:
Image Credit: Zina Deretsky, National Science Foundation via Public domain
More about our data sources and methodologies.
Featured Schools
 Request Info
Request Info
|
Southern New Hampshire University You have goals. Southern New Hampshire University can help you get there. Whether you need a bachelor's degree to get into a career or want a master's degree to move up in your current career, SNHU has an online program for you. Find your degree from over 200 online programs. Learn More > |
