What is a Genetic Counselor?
Genetic Counselor Example Assess individual or family risk for a variety of inherited conditions, such as genetic disorders and birth defects. Provide information to other healthcare providers or to individuals and families concerned with the risk of inherited conditions. Advise individuals and families to support informed decisionmaking and coping methods for those at risk. May help conduct research related to genetic conditions or genetic counseling.
Daily Life Of a Genetic Counselor
- Analyze genetic information to identify patients or families at risk for specific disorders or syndromes.
- Collect for, or share with, research projects patient data on specific genetic disorders or syndromes.
- Explain diagnostic procedures such as chorionic villus sampling (CVS), ultrasound, fetal blood sampling, and amniocentesis.
- Provide genetic counseling in specified areas of clinical genetics, such as obstetrics, pediatrics, oncology and neurology.
- Determine or coordinate treatment plans by requesting laboratory services, reviewing genetics or counseling literature, and considering histories or diagnostic data.
- Assess patients’ psychological or emotional needs, such as those relating to stress, fear of test results, financial issues, and marital conflicts to make referral recommendations or assist patients in managing test outcomes.
Skills Needed to be a Genetic Counselor
When polled, Genetic Counselors say the following skills are most frequently used in their jobs:
Reading Comprehension: Understanding written sentences and paragraphs in work related documents.
Active Listening: Giving full attention to what other people are saying, taking time to understand the points being made, asking questions as appropriate, and not interrupting at inappropriate times.
Complex Problem Solving: Identifying complex problems and reviewing related information to develop and evaluate options and implement solutions.
Social Perceptiveness: Being aware of others’ reactions and understanding why they react as they do.
Speaking: Talking to others to convey information effectively.
Critical Thinking: Using logic and reasoning to identify the strengths and weaknesses of alternative solutions, conclusions or approaches to problems.
Types of Genetic Counselor
- Prenatal Genetic Counselor
- Cancer Genetics Assistant
- Genetics Counselor
- Certified Genetic Counselor
- Staff Genetic Counselor
Job Opportunities for Genetic Counselors
There were about 3,100 jobs for Genetic Counselor in 2016 (in the United States). New jobs are being produced at a rate of 29% which is above the national average. The Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts 900 new jobs for Genetic Counselor by 2026. Due to new job openings and attrition, there will be an average of 300 job openings in this field each year.

The states with the most job growth for Genetic Counselor are Utah, Arizona, and Colorado. Watch out if you plan on working in Nebraska, Idaho, or Missouri. These states have the worst job growth for this type of profession.
How Much Does a Genetic Counselor Make?
The typical yearly salary for Genetic Counselors is somewhere between $52,750 and $107,450.

Genetic Counselors who work in Texas, California, or Nevada, make the highest salaries.
How much do Genetic Counselors make in each U.S. state?
| State | Annual Mean Salary |
|---|---|
| Alabama | $48,800 |
| Arizona | $80,160 |
| California | $89,530 |
| Colorado | $87,290 |
| District of Columbia | $79,300 |
| Florida | $54,730 |
| Georgia | $82,370 |
| Illinois | $83,580 |
| Indiana | $74,950 |
| Maryland | $68,370 |
| Massachusetts | $83,540 |
| Michigan | $71,710 |
| Minnesota | $78,550 |
| Missouri | $72,780 |
| Nevada | $95,830 |
| New Jersey | $85,420 |
| New York | $86,810 |
| North Carolina | $71,600 |
| Ohio | $77,110 |
| Oregon | $80,870 |
| Pennsylvania | $73,410 |
| South Carolina | $81,140 |
| Tennessee | $75,680 |
| Texas | $92,960 |
| Utah | $85,330 |
| Washington | $84,450 |
| Wisconsin | $82,070 |
What Tools do Genetic Counselors Use?
Although they’re not necessarily needed for all jobs, the following technologies are used by many Genetic Counselors:
- Microsoft Excel
- Microsoft Word
- Microsoft Office
- Microsoft PowerPoint
- Web browser software
- Microsoft Access
- Database software
- FileMaker Pro
How to Become a Genetic Counselor
Education needed to be a Genetic Counselor:
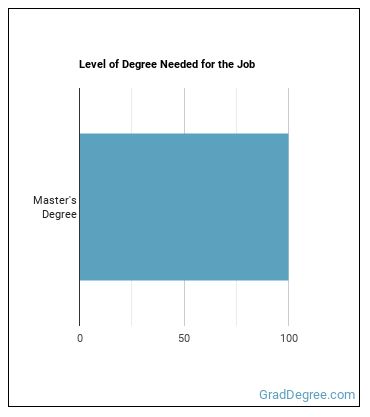
What work experience do I need to become a Genetic Counselor?

Where Genetic Counselors Work

Below are examples of industries where Genetic Counselors work:

You May Also Be Interested In…
Those interested in being a Genetic Counselor may also be interested in:
References:
Image Credit: Staff Sgt. Katie Spencer via Public domain
More about our data sources and methodologies.
Featured Schools
 Request Info
Request Info
|
Southern New Hampshire University You have goals. Southern New Hampshire University can help you get there. Whether you need a bachelor's degree to get into a career or want a master's degree to move up in your current career, SNHU has an online program for you. Find your degree from over 200 online programs. Learn More > |
