What Do Cytotechnologist Do?
Cytotechnologist Example Stain, mount, and study cells to detect evidence of cancer, hormonal abnormalities, and other pathological conditions following established standards and practices.
A Day in the Life of a Cytotechnologist
- Maintain effective laboratory operations by adhering to standards of specimen collection, preparation, or laboratory safety.
- Examine specimens, using microscopes, to evaluate specimen quality.
- Examine cell samples to detect abnormalities in the color, shape, or size of cellular components and patterns.
- Perform karyotyping or organizing of chromosomes according to standardized ideograms.
- Examine specimens to detect abnormal hormone conditions.
- Prepare and analyze samples, such as Papanicolaou (PAP) smear body fluids and fine needle aspirations (FNAs), to detect abnormal conditions.
Featured schools near , edit
Skills Needed to be a Cytotechnologist
When polled, Cytotechnologists say the following skills are most frequently used in their jobs:
Critical Thinking: Using logic and reasoning to identify the strengths and weaknesses of alternative solutions, conclusions or approaches to problems.
Active Listening: Giving full attention to what other people are saying, taking time to understand the points being made, asking questions as appropriate, and not interrupting at inappropriate times.
Reading Comprehension: Understanding written sentences and paragraphs in work related documents.
Active Learning: Understanding the implications of new information for both current and future problem-solving and decision-making.
Judgment and Decision Making: Considering the relative costs and benefits of potential actions to choose the most appropriate one.
Speaking: Talking to others to convey information effectively.
Related Job Titles for this Occupation:
- Cytologist
- Senior Cytotechnologist
- Cytology Manager
- Specimen Preparation Assistant
- Cytology Supervisor
What Kind of Cytotechnologist Job Opportunities Are There?
In the United States, there were 171,400 jobs for Cytotechnologist in 2016. New jobs are being produced at a rate of 11.6% which is above the national average. The Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts 19,800 new jobs for Cytotechnologist by 2026. Due to new job openings and attrition, there will be an average of 12,900 job openings in this field each year.

The states with the most job growth for Cytotechnologist are Utah, Colorado, and Arizona. Watch out if you plan on working in Rhode Island, Connecticut, or Illinois. These states have the worst job growth for this type of profession.
Tools & Technologies Used by Cytotechnologists
Although they’re not necessarily needed for all jobs, the following technologies are used by many Cytotechnologists:
- Microsoft Excel
- Microsoft Word
- MEDITECH software
- Laboratory information system LIS
- Sunquest Information Systems Sunquest Laboratory
- STARLIMS
- CPSI CPSI System
- Orchard Software Orchard Harvest LIS
- Healthvision TDSynergy LIS
- Comp Pro Med Polytech
- Custom Software Systems StarLab
- Elekta Impac Software IntelliLab
- EpicLab Laboratory Information System
- Fletcher-Flora Health Care Systems FFlex eSuite LIS
- Fletcher-Flora Health Care Systems LabPak LIS
- GE Healthcare Centricity Laboratory
- HEX Laboratory Systems LAB/HEX
- Clinical Software Solutions CLIN1 Suite
- LabSoft LabNet
- ClinLab LIS
Becoming a Cytotechnologist
Learn what Cytotechnologist education requirements there are.
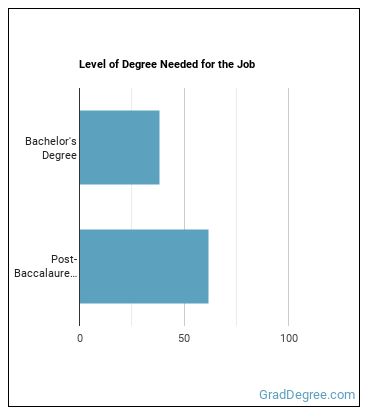
What work experience do I need to become a Cytotechnologist?

References:
Image Credit: Staff Sgt. Jerilyn Quintanilla via U.S. Air Force photo
More about our data sources and methodologies.
Featured Schools
 Request Info
Request Info
|
Southern New Hampshire University You have goals. Southern New Hampshire University can help you get there. Whether you need a bachelor's degree to get into a career or want a master's degree to move up in your current career, SNHU has an online program for you. Find your degree from over 200 online programs. Learn More > |
